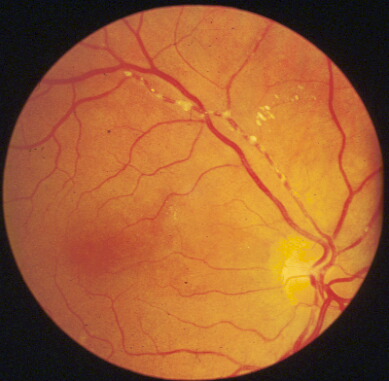
Branch retinal artery occlusion
|
||
|
In the examination you are unlikely to get a case of cherry red spot from central retinal artery because the sign usually disappears after 72 hours. Most cases of central retinal artery will be presented as optic atrophy or relative afferent pupillary defect. On the other hand, signs from emboli tend to remain longer and therefore more likely to appear in the examination. The retinal artery shows cattle-trackings with multiple
emboli. The emboli may be shiny if due to cholesterol crystals
Mention that you would like to:
|
Questions:
1. What are the types of emboli which can cause branch
retinal artery occlusion?