Myasthenia gravis
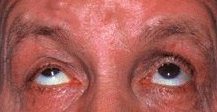
Right ptosis due to myasthenia gravis showing fatiguability
of the right lid on sustained upgaze
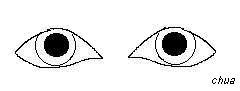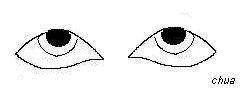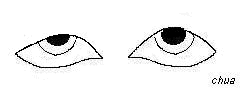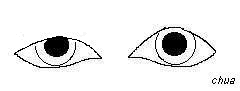
This is also called the Simpson test in which fatigure
is observed on sustained lid and eye elevation. |
a |
There is a right partial ptosis. The pupils are equal
in size. There may be limitation of ocular movement in any combination.
The vertical muscles tend to be affected most. The limitation is variable
and does not appear to correspond to any nerve palsy. On sustained upgaze,
the right upper lid shows increased ptosis.
Perform the following:
-
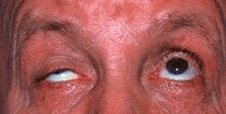
Cogan's lid twitch sign = get the patient to rapidly refixate
their eye from downgaze to the primary position, the sign is positive if
there is overshooting of the upper lid before settling down to the ptotic
position
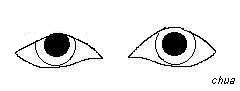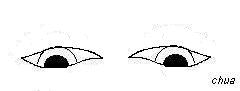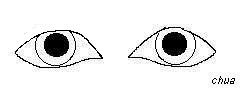
Animated pitcutre of a patient with right Cogan's twitch
sign on rapid upgaze. Note the overshooting of the lid before settling
down to the original ptotic level. |
-
look for other signs of myasthenia gravis: thoracic scar
from thymomectomy and weak voice.
|
Questions:
1. During the Tensilon test, a patient collapses. How
would you manage the patient?