These two patients who recently had had forehead botox rejuvenation complained of heavy eyelids and problems of applying make-up to the upper lids. On examination, they were found to have bilateral dermatochalasis which were not present before botox injection. The dermatochalasis in these two patients were previously compensated by unconscious frontalis overaction. Following botox injection, the frontalis action is removed leading to lower eyebrows position and hence the appearance of redundant skin. The problem may be anticipated by stabilizing the frontalis and note any signs of dermatochalasis prior to the botox injection. Any evidence of dermatochalasis should be noted and explained to the patient. There are two ways of getting around these problems: First, the injection was given only to the upper part of the frontalis with the hope of avoiding complete frontalis paralysis Second, patients are told about the possible need for blepharoplasty if dermatochalasis develop. |
|
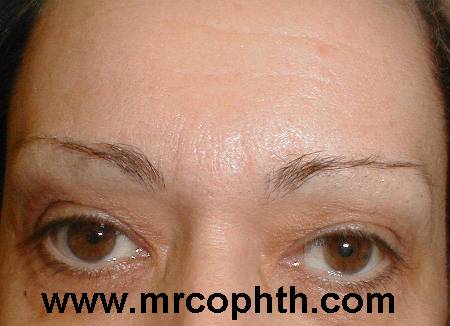
Patient 1: medial dermatochalsis and smooth forehead |
|
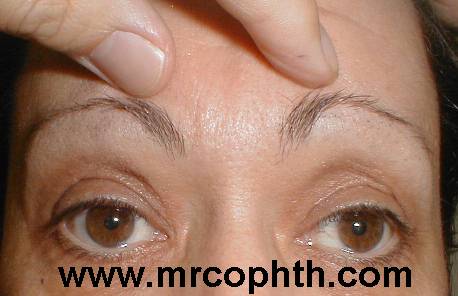
Patient 1: manual elevation of the eyebrows reduces the dermatochalsis |
|
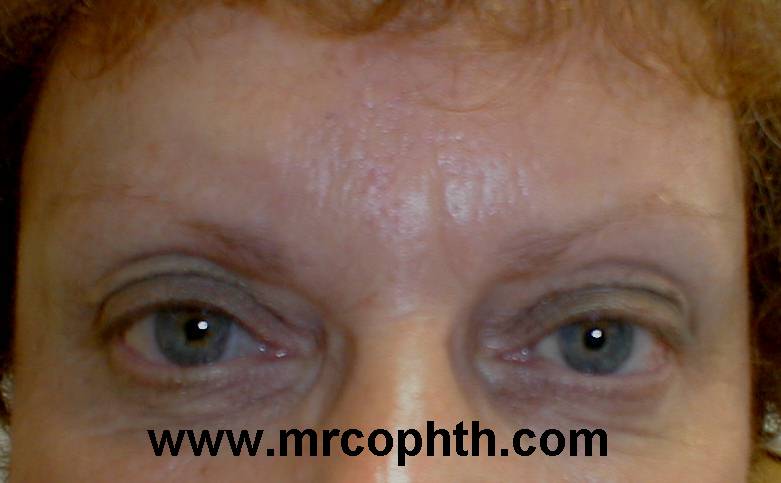
Patient 2: additional folds of skin above the skin crease. Again the smooth forehead. |
|
|