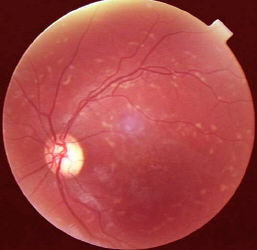
Stargardt's disease / fundus flavimaculatus
|
|
| The posterior pole contains yellow
flecks with indistinct border (so called fish scale or pisciform lesions,
the lesions are lipofuscin found within the RPE). There is retinal pigment epithelium atrophy in the fovea (so called bronze beaten appearance, there may be exposure of the choroidal blood vessels). The condition is an inherited bilateral disorders (autosomal recessive being the commonest and occasionally autosomal dominant). Other signs:
Stargardt's disease, the only lesion may be atrophic foveal lesions. Therefore, always include Stargardt's disease in your differentiatial diagnosis in any young patients with bilateral macular atrophy. . |
Questions:
1. What is the differential diagnosis of Stargardt's disease?