Lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg's Syndrome)
|
|||
|
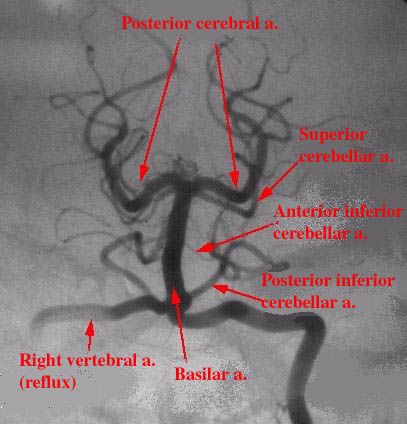
This condition is caused by vascular occlusion or haemorrhage of the lateral medulla and often results from a lesion in the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The signs result from damages to the structures in the lateral medulla which include: the sympathetic pathway, Vth cranial nerve, vestibular nuclei, inferior cerebellar peduncle, IXth and Xth cranial nerves. The patient has a Horner's syndrome with nystagmus, The
fast phase is to the side of the Horner's syndrome. There is
Further examination:
|
Questions:
Can you name a few eponymous syndromes resulting from
brainstem infarction with ocular signs.